Measuring Partial Discharge On Operating High Voltage Motors With Vs-pwm Variable Speed Drives
G.C. Stone, H.G. Sedding, C. Chan Iris Power – Qualitrol, Mississauga, ON, Canada
ABSTRACT
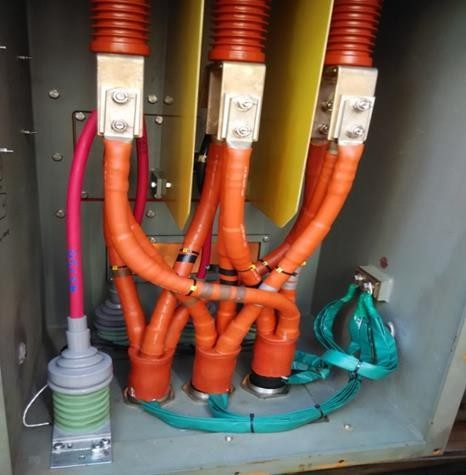
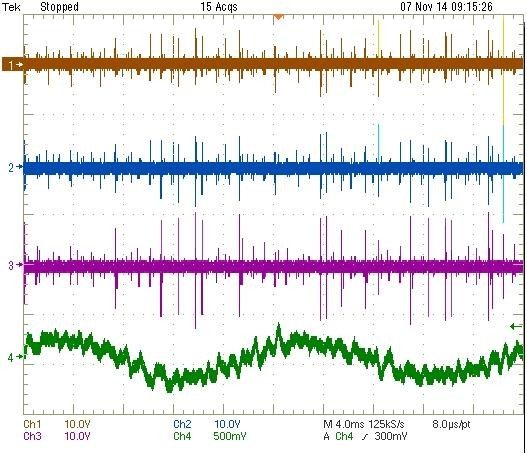
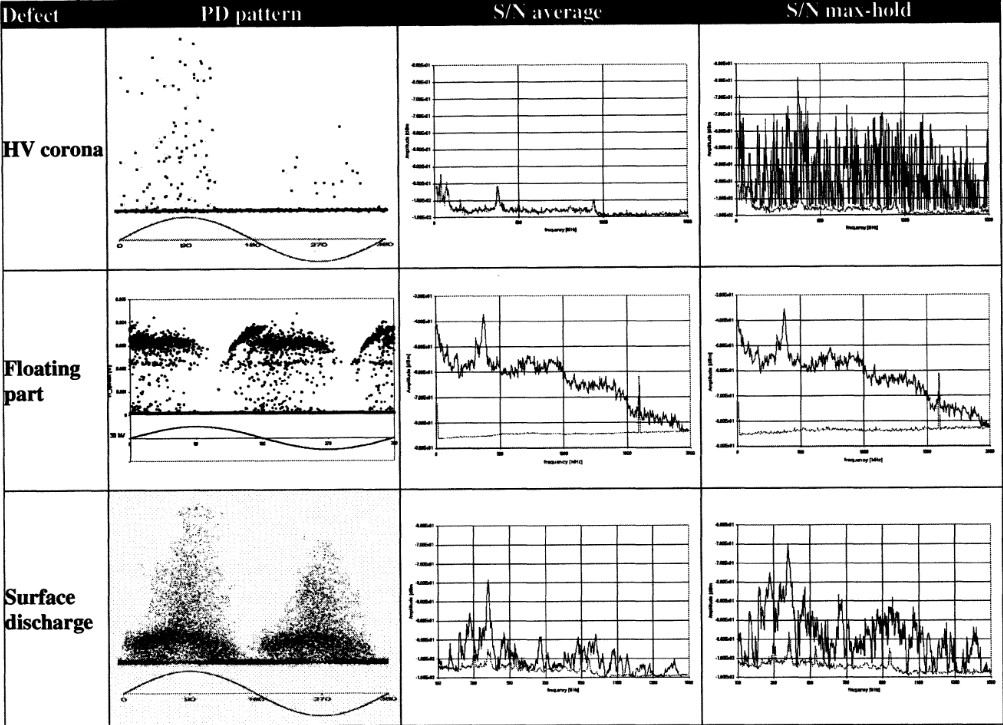
Inverter fed motors (IFMs) are now widely being applied in petrochemical plants to vary the speed and power of a motor to improve processing and reduce energy costs. IFMs of the voltage source, pulse width modulation (VS-PWM) type have become the most popular type of drive due to their relatively small size and low cost. Unfortunately, the voltage transients created by such IFMs are similar to the pulse signals caused by stator winding partial discharges, and thus distinguishing stator winding PD becomes harder.
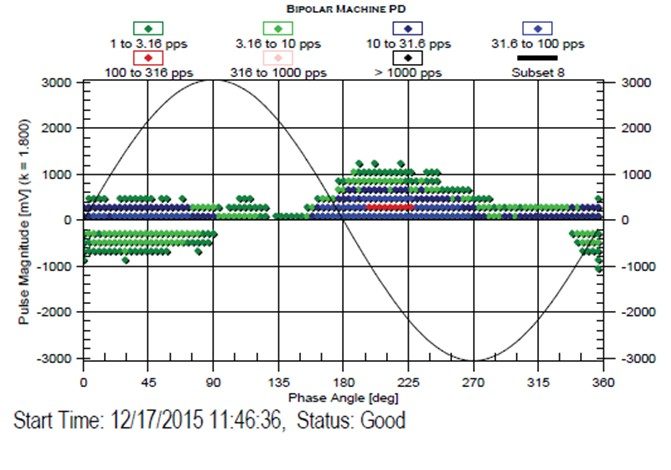
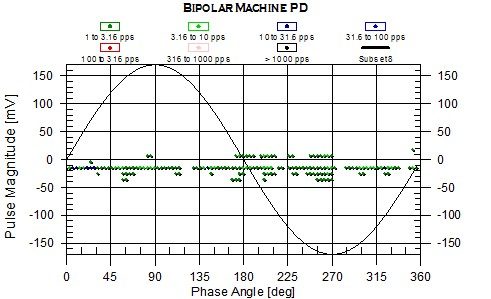
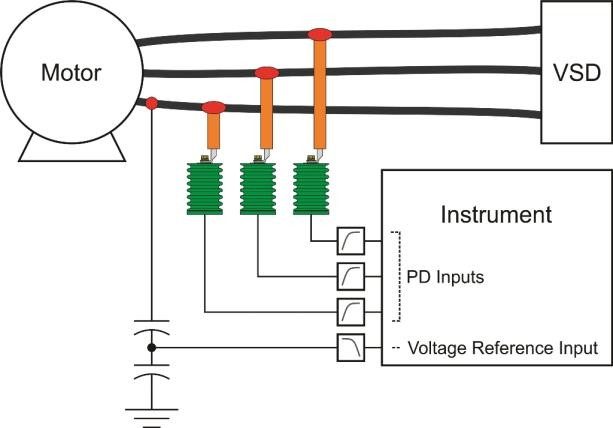
Several decades of experience indicates that the trend in PD activity over time can help users detect developing stator winding insulation problems in conventional motors rated 3.3 kV and above, and users can then plan maintenance actions based on the measurement findings. A multi-year research project was undertaken to develop an on-line PD monitoring system that can better detect PD in IFMs, without being overwhelmed by noise from the inverter. This paper briefly outlines the difficulties in measuring PD on IFMs of the VS-PWM type, describes the monitoring system developed, and gives case studies from installations around the world.
Keywords: Inverter Fed Motors, Electrical Insulation Failure, Partial Discharge Testing.